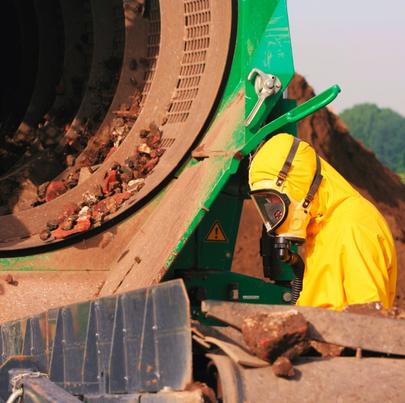
More than 20 percent of the workforce in the United States (over 32 million workers) is exposed to hazardous substances on the job. These hazardous substances can enter the body in several ways, including absorption through the skin, inhalation, and accidental ingestion or injection. Employers are responsible for creating processes and procedures that minimize their employees’ exposure to hazardous substances at worksites. When they fail with their responsibilities, injured workers have a right to seek assistance from a work injury attorney to recover compensation.

Dangers of Hazardous Substances
Almost three million hazardous substance exposures occur in private industries each year with half resulting in serious injuries that lead to lost time at work.
With over 650,000 different chemicals found in more than three million workplaces across the United States, exposure is common. However, there are several hazardous substances that are more noteworthy than others, and exposure can occur in a variety of ways.
Asbestos
Used as fire insulation, asbestos is a carcinogen that has been linked to mesothelioma, a rare form of cancer. Asbestos fibers that are inhaled can cause lung damage and cancer.
Lead
Used in older paints, pipes, and glazing, lead is a category 2 carcinogen. It has been linked to cancer, kidney damage, central nervous system problems and infertility from exposure.
Respirable Crystalline Silica
OSHA began enforcing rules concerning use of crystalline silica in construction in October 2017. It has been classified as a group one human carcinogen. Exposure through inhalation can also cause COPD, silicosis and other severe lung conditions.
Hexavalent Chromium
Hexavalent chromium is a known carcinogen that is found in Portland cement and is associated with welding stainless and galvanized steel. In addition to cancer, exposure to the skin or eyes can cause permanent damage from chemical burns.
Formaldehyde
Workplace exposure to formaldehyde has been recently linked to a risk of developing leukemia. It had previously been linked to respiratory cancers through inhalation.
Preventing Exposure to Toxins
The key to preventing exposure is to provide workers with information about the chemicals used in the workplace and their hazards. Under OSHA’s Hazard Communication Standard (HCS), if hazardous chemicals are used in the workplace, an employer must:
- Label the chemicals as hazardous.
- Advise workers of hazards associated with chemicals in their work area.
- Provide exposed workers with material safety data sheets (MSDS) and protective equipment.
- Train workers in the safe handling of the chemicals and what methods should be used for protection.